| name | parameter function | short description |
|---|---|---|
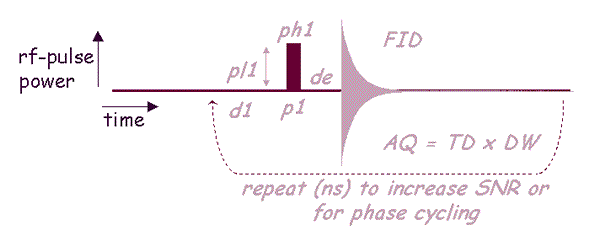
| zg | pulse program | A set of instructions to the spectrometer telling it when to wait, when to pulse, and when to acquire. The zg experiment is the single pulse-acquire routine shown above. |
| d1 | recycle delay | The delay between the end of acquisition and the next scan. |
| p1 | pulse length | The radio-frequency (rf)-pulse time in microseconds. |
| pl1 | pulse power level | The attenuation applied to the amplifier’s output. |
| de | dead time | The time the spectrometer waits between the end of the final pulse and the start of detection. It allows for probe ring-down to end before beginning data collection. |
| aq | acquisition | The total time that digitization of the “free induction decay” (FID) takes place. aq = dw * td = td / (2swh) |
| td | time domain points | The number of points used to digitize the FID. |
| dw | dwell time | The time interval between the sampled points (td) of the FID. dw = 1 / (2swh) |
| sw | spectral width | The frequency range of the acquired spectrum in ppm. If the units are in Hz, the parameter is swh. swh=1/(2*dw) |
| ns | number of scans | The number of repetitions of the experiment. The more FID’s added together, the higher the signal-to-noise ratio. |
| ds | dummy scan | The number of time that the full experiment is repeated, but the FID is not stored. It is used to establish an equilibrium between pulses and delays before storing data. |
| o1p | offset | The center frequency of the RF pulse (the carrier frequency) translated into ppm (the center of the spectrum after Fourier transform). The same value in absolute units (MHz) is called sfo1. Or in Hz, relative to TMS, is called o1. |


